Epithelial Tissues
They are a vital component of our body's structure and function. They line the surfaces of organs, cavities, and blood vessels, providing protection, absorption, and secretion.
Squamous epithelium
- Made up of thin, flattened and irregularly shaped cells.
- Forms the outer layer of the skin, inner lining of the blood vessels and air sacs of the lungs (alveoli)
- Main function is protection
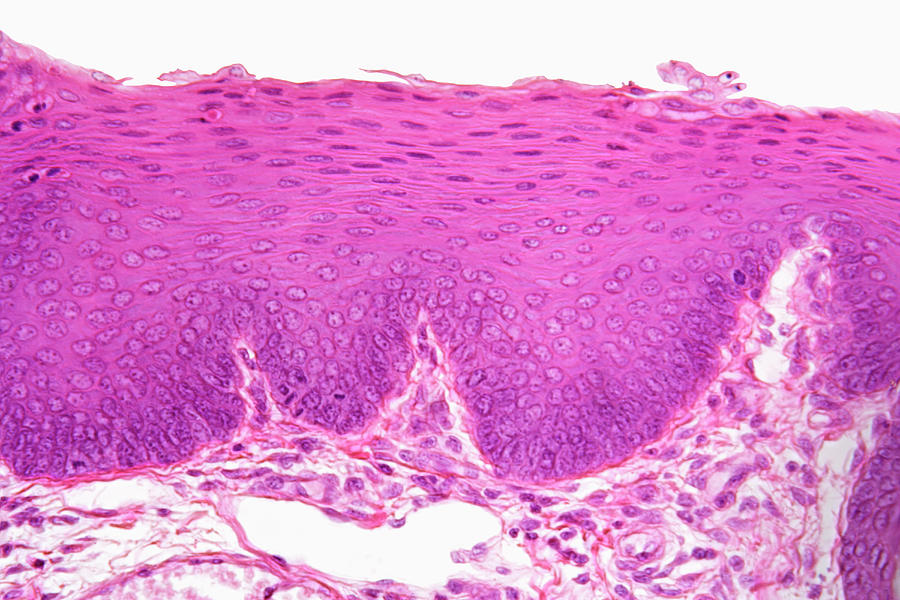
Stratified Squamous epithelium
- Cells are arranged in many layers, each layer consisting of different types of cells
- Deeper layers have cuboidal cells which become polygonal and finally flattened towards the free surface
- Found in the skin and covers the external dry surface Columnar epithelium
- Made up of tall, cylindrical or column-like cells.
- Forms the inner lining of stomach, intestines, pharynx and larynx
- Facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier Ciliated epithelium
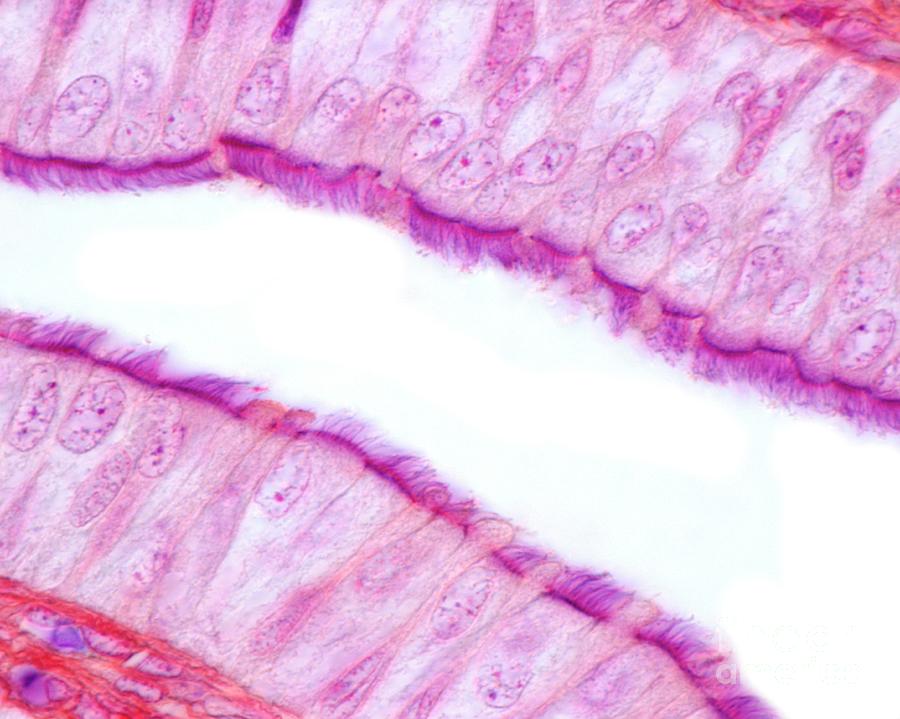
- Made of columnar epithelium with hairlike protrusions called cilia
- Found in the nasal passages and bronchioles
- Main function is protection, secretion and absorption Cuboidal epithelium
- Made up of cube shaped cells
- Forms the lining of thyroid glands and kidney tubules
- Main function is secretion and absorption
Squamous epithelium
- Made up of thin, flattened and irregularly shaped cells.
- Forms the outer layer of the skin, inner lining of the blood vessels and air sacs of the lungs (alveoli)
- Main function is protection
Stratified Squamous epithelium
- Cells are arranged in many layers, each layer consisting of different types of cells
- Deeper layers have cuboidal cells which become polygonal and finally flattened towards the free surface
- Found in the skin and covers the external dry surface Columnar epithelium
- Made up of tall, cylindrical or column-like cells.
- Forms the inner lining of stomach, intestines, pharynx and larynx
- Facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier Ciliated epithelium
- Made of columnar epithelium with hairlike protrusions called cilia
- Found in the nasal passages and bronchioles
- Main function is protection, secretion and absorption Cuboidal epithelium
- Made up of cube shaped cells
- Forms the lining of thyroid glands and kidney tubules
- Main function is secretion and absorption



Comments
Post a Comment