THE LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics dealing with heat and temperature and their relation to energy and work. It deals with the behavior of systems that are in thermal equilibrium or approaching it,and provides the laws that govern the direction and magnitude of heat transfer.
1st Law of Thermodynamics
The total energy of a closed system remains constant, although energy can be transformed from one form to another. It is expressed as ΔU = Q - W, where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is heat added to the system, and W is work done by the system.
The entropy of a closed system will always increase over time, leading to thermal equilibrium. It is stated as "Heat flows spontaneously from hot to cold." It is expressed as ΔS ≥ Q/T, where ΔS is the change in entropy, Q is heat, and T is temperature.
As the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, its entropy approaches a minimum value. At absolute zero, a perfect crystal will have zero entropy.
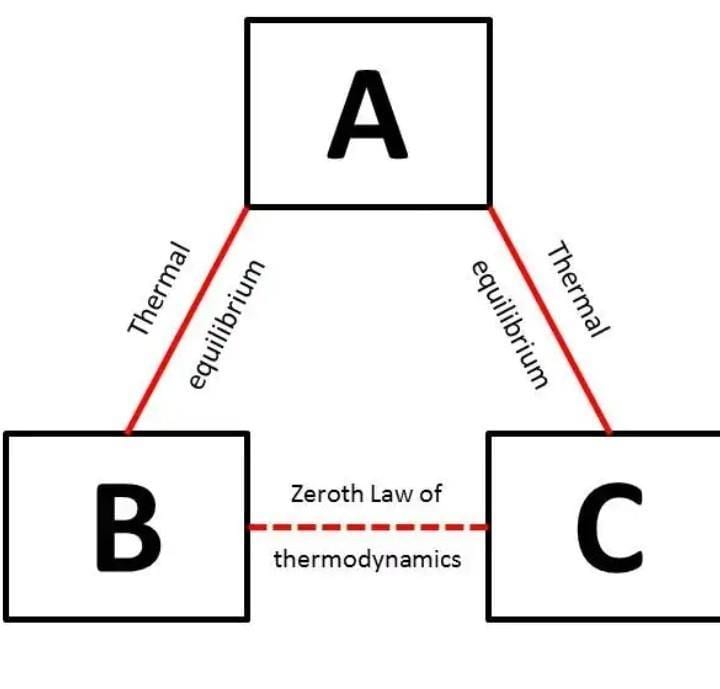
If body A and B are in equilibrium with each other and body B and C are in equilibrium with each other then body A and C will be in equilibrium with each other.



Comments
Post a Comment